
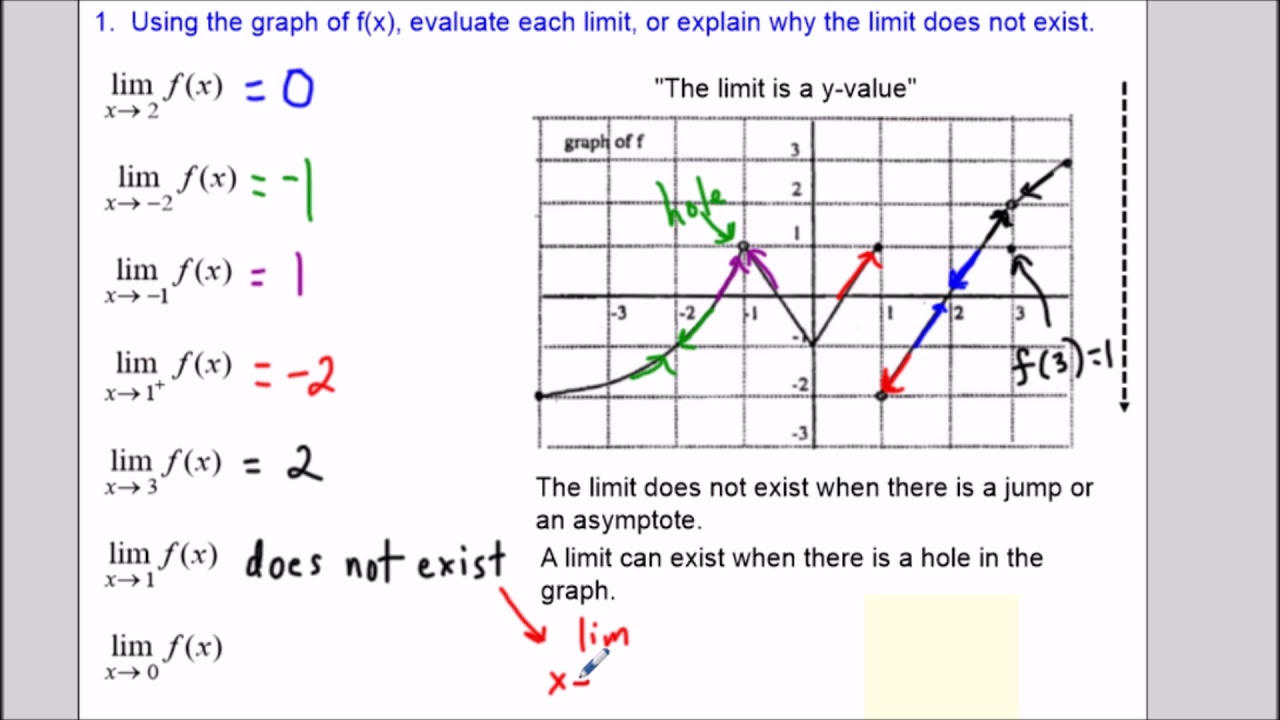
A function f (x) is continuous at a point x a if f (a) exists lim f (x) exists i.e. Graphical meaning and interpretation of continuity are also included. The mathematical definition of the continuity of a function is as follows. These gaps or breaks can be easily seen in a graph. The continuity of a function and its derivative at a given point is discussed. Proving that a limit exists using the definition of a limit of a function of two variables can be challenging.

The smaller the value of, the smaller the value of. The graph in the last example has only two discontinuities since there are only two places where we would have to pick up our pencil in sketching it. Figure 14.2.2: The limit of a function involving two variables requires that f(x, y) be within of L whenever (x, y) is within of (a, b). In contrast, the function M( t) denoting the amount of money in a bank account at time t would be considered discontinuous, since it "jumps" at each point in time when money is deposited or withdrawn.Ī form of the epsilon–delta definition of continuity was first given by Bernard Bolzano in 1817. What is Continuity in Calculus A function is continuous when there are no gaps or breaks in the graph. A function is continuous on an interval if we can draw the graph from start to finish without ever once picking up our pencil. In order theory, especially in domain theory, a related concept of continuity is Scott continuity.Īs an example, the function H( t) denoting the height of a growing flower at time t would be considered continuous. The latter are the most general continuous functions, and their definition is the basis of topology.Ī stronger form of continuity is uniform continuity. The concept has been generalized to functions between metric spaces and between topological spaces. The epsilon–delta definition of a limit was introduced to formalize the definition of continuity.Ĭontinuity is one of the core concepts of calculus and mathematical analysis, where arguments and values of functions are real and complex numbers. Up until the 19th century, mathematicians largely relied on intuitive notions of continuity, and considered only continuous functions. lim x a f ( x) f ( a) lim x a f ( x) f ( a) A function is discontinuous at a point a if it fails to be continuous at a. A discontinuous function is a function that is not continuous. At which of the x values are all three requirements for continuity satisfied Answers and explanations All three requirements for the existence of a limit are satisfied at the x values 0, 4, 8, and 10: At 0, the limit is 2. Intuitively, a continuous function is one whose graph can be drawn without lifting the pencil off of the paper.
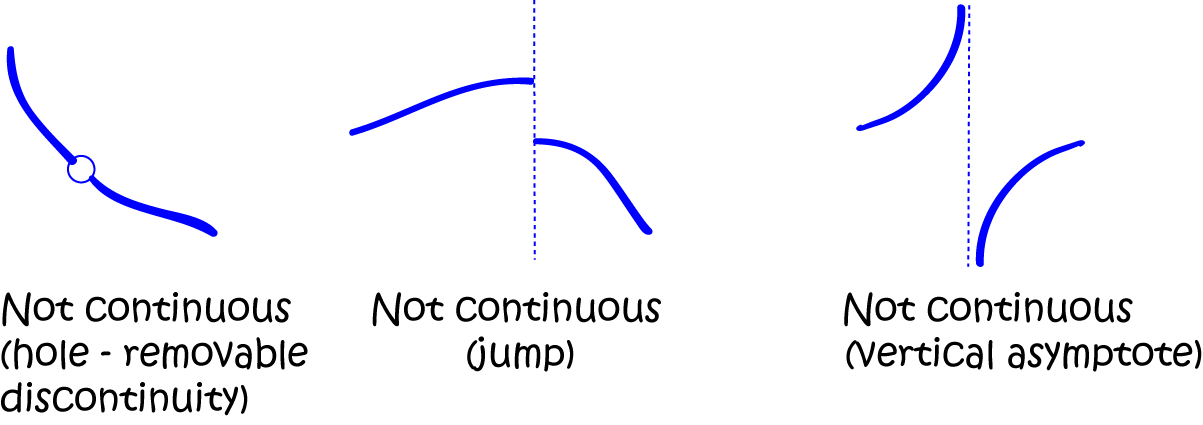
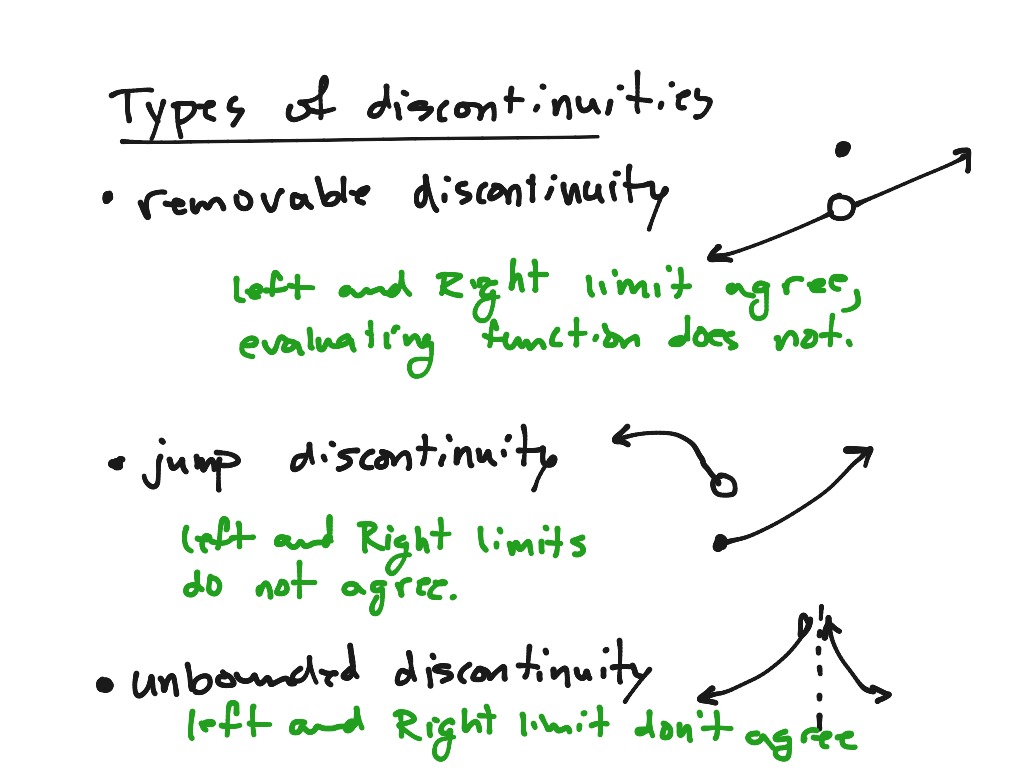
More precisely, a function is continuous if arbitrarily small changes in its value can be assured by restricting to sufficiently small changes of its argument. Continuity Limits can be used to give precise meaning to the concept of continuity. This means that there are no abrupt changes in value, known as discontinuities. The behavior at \( x = 3 \) is called a jump discontinuity, since the graph jumps between two values.In mathematics, a continuous function is a function such that a continuous variation (that is a change without jump) of the argument induces a continuous variation of the value of the function. The behaviors at \(x = 2\) and \(x = 4\) exhibit a hole in the graph, sometimes called a removable discontinuity, since the graph could be made continuous by changing the value of a single point.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
